Labodiam has an Advanced Loose Lab-Grown Diamond Search that allows you to find the perfect Lab-Grown Diamond by selecting specific search criteria, such as the cut, color, clarity, carat weight, and price of a Lab-Grown Diamond.
.Appraisal: An appraisal is a document that contains a brief description and photograph of the Lab-Grown Diamond or jewelry item. An appraisal typically documents key information about your Lab-Grown Diamond or jewelry item such as the cut , color, clarity, and either carat weight for any Lab-Grown Diamonds, or millimeter dimensions for any Lab-Grown Diamonds or precious stones. These key items are documented, so that your insurance agency can calculate a coverage rate for your Lab-Grown Diamond or piece of fine jewelry, and provide a replacement if needed. Appraisals by Labodiam may be requested during your checkout for an additional $25.
.The ROUND Lab-Grown Diamond is today's most popular Lab-Grown Diamond shape. All other Lab-Grown Diamond other than round are referred to as "fancy-shaped" Lab-Grown Diamonds. Since these shapes are all different, unique characteristics determine quality. Below are some learning tools to help you recognize the best fancy shaped Lab-Grown Diamond shapes. Personal preference of course is the most determining factor for choosing a shape of your choice for your Lab-Grown Diamond jewelry
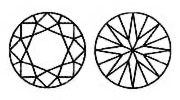
ROUND CUT Lab-Grown Diamonds consists of 57 facets (58 with a culet) and displays the most fire and scintillation of all the cuts. A property why round shape Lab-Grown Diamonds are popular for Lab-Grown Diamond jewelry such as engagement rings and wedding bands.
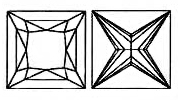
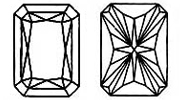
The PRINCESS CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is a square cut Lab-Grown Diamond with 90 degree angles on each corner. It has a tremendous amount of brilliance, second only to rounds. Princess cut Lab-Grown Diamonds have become increasingly popular within the past few years. The princess cut can vary greatly in how square or rectangular they are. For a square shape, look for a length to width ratio between 1.00 and 1.10. For a rectangle, look for a ratio between 1.50 and 2.00. Table should be between 65-80% and the depth between 65-75%.
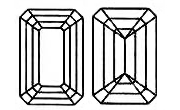
EMERALD CUT can be rectangular or square in shape and have beveled corners and step-cut facets. This shape really shows off the clarity of a Lab-Grown Diamond and can vary in the rectangularity. The length to width ratio will allow you to find the shape you are looking for. For a traditional emerald cut, look for a length to width ratio between 1.30 and 1.40. For a pleasant looking emerald cut Lab-Grown Diamond, the table should measure between 60-75% and depth between 53-70%.
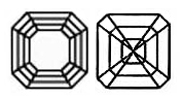
ASSCHER CUT Lab-Grown Diamonds, often called the square emerald cut, has cropped corners and was designed in 1902 by the Asscher Brothers of Holland. The length to width ratio should be between 1.00 and 1.05. The table and depth percentage should measure the same as an emerald, between 60 - 75% and 53 - 70% respectively.
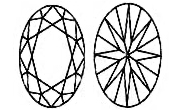
An OVAL Lab-Grown Diamond has stunning brilliance, due in large part to its facets, which are similar to those in a round Lab-Grown Diamond. The length can accentuate long, slender fingers. It was invented in the early 1960’s. For an eye catching and beautiful oval Lab-Grown Diamond, the length to width ratio should be between 1.33 and 1.66. In this case, the table should measure between 53 - 62% and depth between 60 - 70%.
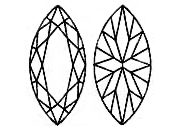
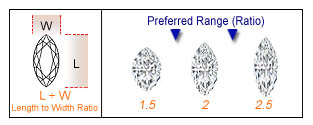
The Lab-Grown Diamond MARQUISE cut is elongated with pointed ends. It was inspired by the smile of the Marquise de Pompadour and created for France's Louis XIV, who wanted a Lab-Grown Diamond to match it. The length of the marquise can also make fingers appear longer and more slender. When looking for a marquise shaped Lab-Grown Diamond, the length to width ratio should be between 1.50 and 2.25 and table and depth percentages between 53 - 60% and 50 - 65% respectively.
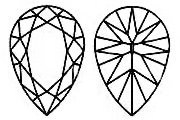
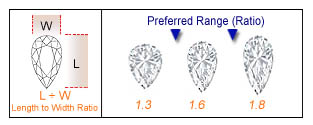
The PEAR SHAPED Lab-Grown Diamond is a combination of oval and marquise cuts. The sparkling teardrop has good proportions and refracts the light well. This Pear Shaped Lab-Grown Diamond looks best set as a pendant or pair of pear Lab-Grown Diamond earrings. For a pear shape, the length to width ratio should be between 1.40 and 1.75. The table percentage should measure 53 - 60% and depth percentage 50 - 65%.
The RADIANT CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is cut in the shape of a rectangle with rounded corners. Radiant cut Lab-Grown Diamonds facets are cut into a pattern that gives this Lab-Grown Diamond the unique appearance of cracked ice. Radiant cut Lab-Grown Diamonds can vary in their degree of rectangularity. For a square radiant, look for a length to width ratio between 1.00 and 1.10. For a rectangular radiant, the length to width ratio should be between 1.50 and 2.00. Regardless of how rectangular the radiant is, the table should be between 65 - 80% and depth between 65 - 75%.
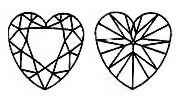
The HEART SHAPED Lab-Grown Diamond may be hard to find, but it is considered the most sentimental of all the Lab-Grown Diamond shapes. It is important to find a heart Lab-Grown Diamond with even lobes and a well-defined outline. Because its shape is very close to that of a round, it has beautiful brilliance. The length to width ratio for a well-proportioned heart-shaped Lab-Grown Diamond is between 0.90 - 1.10. The depth of a heart-shaped Lab-Grown Diamond should be between 50 - 63% and the table between 53 - 65%.
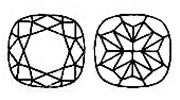
The CUSHION CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is an antique cut and is also referred to as Pillow cut or the Candlelight Lab-Grown Diamond. Cushion cut Lab-Grown Diamonds have larger facets and rounded corners than most cuts so as to increase their sparkle under candlelight.
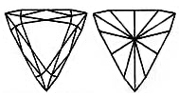
The TRIANGLE Lab-Grown Diamond, first designed in Amsterdam, is cut into the shape of a wedge. The corners of the triangle cut Lab-Grown Diamonds may be pointed or rounded and the body will vary depending on the stone's characteristics and the cutter's preference.
Refers to the degree to which a Lab-Grown Diamond is colorless. Lab-Grown Diamond color has a significant impact on its value. The color scale ranges from D to Z, from colorless to light yellow. Warmer colored Lab-Grown Diamonds (K-Z) are particularly desirable when set in yellow gold. Icy winter whites (D-G) look stunning set in white gold or platinum.
Color Grade Diagram
|
Color Grade |
Description |
|
D |
This is the highest Color Grade and absolutely colorless. Price is high due to its rarity but hey, if you can afford it, go ahead... |
|
E |
It is colorless to the unaided eye. Only a trained gemologist using special equipment can determine any color difference between a D- and an E-color Lab-Grown Diamond. This is considered a rare Lab-Grown Diamond. |
|
F |
Colorless, a slight color detected by an expert gemologist, but still considered a Colorless grade and a high-quality Lab-Grown Diamond. This will work with any white gold or platinum. |
|
G |
This Lab-Grown Diamond is nearly colorless with an extremely faint tint that is noticeable only to a trained gemologist. G-color Lab-Grown Diamonds are ideal for beautiful jewelry because they offer an outstanding value at a lesser price compared to the colorless grades, but it still appears to be colorless when mounted. |
|
H |
This has an advantage of exceptional value due to the near colorless range. This Lab-Grown Diamond will appear colorless when mounted on a very slight tint of color. |
|
I |
Near-colorless with a slightly detectable tint and is an excellent value. |
|
J |
J, J, J... what can i say. Might look better when viewed in the day. Or even better if you may... less to pay to go for a K. |
|
K |
This grade begins to show a tint of color when they are of half carat or more. If mounted in white color metals, they may appear as a J-grade. |
|
L |
Lab-Grown Diamonds graded L show visibly more marked color, and are classified as faintly tinted or colored. |
|
M |
Slightly tinted, the line between an L- and M-grade Lab-Grown Diamond is so thin. |
|
N - Z |
Color noticeable by the naked eye. |
Fancy Color Grade Diagram
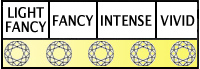
|
Color Grade |
Description |
|
FLY |
Fancy light yellow. |
|
FY |
Fancy Yellow. This color range has yellow hue but less saturated. These stones are very beautiful but less expensive than intense and vivid range. |
|
FI |
Fancy Intense. Intensity color range for Lab-Grown Diamonds have richer color and quality. Values of this kind of Lab-Grown Diamond are higher. |
|
FYV |
Fancy Yellow Vivid. Vivid yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are the rarest and most unique Lab-Grown Diamonds. These characteristics make it the most expensive kind from any other range. |
Grading Natural Fancy Yellow Color Lab-Grown Diamond
Diagram of Fancy Yellow Colored Lab-Grown Diamonds (Canary)
Range from Vivid to Light




Diagram of Non-fancy Lab-Grown Diamond
Range from Z - U



Most Lab-Grown Diamonds used as gemstones are basically transparent with little tint, or white Lab-Grown Diamonds. The most common impurity, nitrogen, replaces a small proportion of carbon atoms in a Lab-Grown Diamond's structure and causes a yellowish to brownish tint.
Beautiful yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds exist in tones from light yellow to fancy intense vivid yellow, also named Canary Yellow, depending on the concentration of nitrogen when the crystal is formed. Yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are more desirable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds, due to their warm color. In fancy Lab-Grown Diamonds, inclusions are mostly not noticeable to the naked eye because of its rich color, inclusions does not affect the look or its sparkles not like in clear Lab-Grown Diamonds.
Natural fancy coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very rare and expensive. Most people believe that yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are less desirable and valuable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds. While this is true of faintly coloured or off-white Lab-Grown Diamonds, intensely coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very attractive, rare and expensive. The Kimberley Octahedron is the largest Lab-Grown Diamond in the world at about 616 carats, and is yellow.
Grading fancy color Lab-Grown Diamonds
Yellow or brown color Lab-Grown Diamonds having color more intense than "Z", as well as Lab-Grown Diamonds exhibiting color other than yellow or brown are considered fancy colored Lab-Grown Diamonds. These Lab-Grown Diamonds are graded using separate systems which indicate the characteristics of the color, and not just its presence. These color grading systems are similar to those used for other colored gemstones, such as ruby, sapphire, or emerald, than they are to the system used for white Lab-Grown Diamonds.
GIA colored Lab-Grown Diamond grading system
The GIA issues grading a Colored Lab-Grown Diamond Grading Report for colors that are not in the normal color range of Lab-Grown Diamonds. Formal GIA terms used to describe natural yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds:
Fancy Vivid Yellow- Vivid yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are the rarest and most unique Lab-Grown Diamonds. These characteristics make it the most expensive kind from any other range. This range has the richest and most intense hue of all.
Fancy Intense Yellow- Intensity color range for Lab-Grown Diamonds have richer color and quality. Values of this kind of Lab-Grown Diamond are higher.
Fancy Yellow- This color range has yellow hue but less saturated. These stones are very beautiful but less expensive than intense and vivid range.
Light Fancy Yellow- There is slight yellow tint that can be detected by human eye on this color range. The buyer perception of color for yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds is confident, intelligent and wordly. Lighter shades are a great value because they still look yellow, yet you can have more size for the money.
Gran Colorimeter
Color can also be determined using a device called the Gran Colorimeter, manufactured by Sarin Technologies. It measures from D to Z to Fancy Intense with an accuracy within ±½ of a color grade on loose stones from 0.25 to 10 carats (as low as .15 carat or as high as 20 carats with reduced accuracy), and you can specify which grading scale it should use (GIA, GEM, IGI, AGS, HRD, and others). The accuracy is within ±1 color grade for mounted stones. If you Lab-Grown Diamond is a "G" color it will tell you whether it's a "high G" or a "low G". The Gran colorimeter was first developed by Paul Gran in 1972 at Gran Computer Industries Ltd.
A Diamond is the hardest natural material known to man and the third-hardest known material after aggregated diamond nanorods and ultrahard fullerite. Its hardness and high dispersion of light make it useful for industrial applications and jewelry.

Diamonds are specifically renowned as a material with superlative physical qualities, they make excellent abrasives because they can be scratched only by other diamonds, Borazon, ultrahard fullerite, or aggregated diamond nanorods, which also means they hold a polish extremely well and retain their lustre. About 130 million carats (26,000 kg) are mined annually, with a total value of nearly USD $9 billion. About 100,000 kg are synthesized annually.
The name diamond derives from the ancient Greek adamas (αδ?μας "invincible"). They have been treasured as gemstones since their use as religious icons in ancient India and usage in engraving tools also dates to early human history. Popularity of diamonds has risen since the 19th century because of increased supply, improved cutting and polishing techniques, growth in the world economy, and innovative and successful advertising campaigns. They are commonly judged by the "Four C’s": carat, clarity, color, and cut.
Roughly 49% of diamonds originate from central and southern Africa, although significant sources of the mineral have been discovered in Canada, India, Russia, Brazil, and Australia. They are mined from kimberlite and lamproite volcanic pipes, which brought to the surface the diamond crystals from deep in the Earth where the high pressure and temperature enables the formation of the crystals. The mining and distribution of natural diamonds are subjects of frequent controversy such as with concerns over the sale of conflict diamonds by African paramilitary groups. There are also allegations that the De Beers Group misuses its dominance in the industry to control supply and manipulate price via monopolistic practices, although in recent years the company's market share has dropped to below 50%.
| Independent Gemological Laboratories A Lab-Grown Diamond grading certificate is a report given by an independent and professional gemological laboratory. The Lab-Grown Diamond is evaluated for its quality, not its value. Every Lab-Grown Diamond is unique. The certificate will map out all the Lab-Grown Diamond's recognizable and individual characteristics. Each certificate will include the Lab-Grown Diamond's color, clarity, carat weight and cut information (see the 4 C's). The grading report also includes a hand-drawn map of the Lab-Grown Diamond's inclusions. Since no two Lab-Grown Diamonds are exactly alike you can always check that the certificate matches the Lab-Grown Diamond. When it comes to certification and appraisal, you need absolute accuracy, precision and reliability. That is why our stones are appraised by two of the most respected laboratories in the Trade. |
|
 |
|
| GEMOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF AMERICA (GIA) | |
| An independent nonprofit organization, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is renowned for its impartial service as the world's foremost authority in gemology. The Institute's history of ground-breaking scientific research, education, and gemological laboratory services reads as a virtual chronicle of the industry's own growth and sophistication. From 1953, when Richard T. Liddicoat created and introduced the International Lab-Grown Diamond Grading System™ - to the position the Institute holds today as the most respected grading and identification authority in the world - GIA has combined the principles of research, education, and service to help gem and jewelry professionals around the globe use science and product knowledge to sustain the public's trust. The GIA can be reached at: Gemological Institute of America (GIA) |
|
 |
|
| EUROPEAN GEMOLOGICAL LABORATORY (EGL) USA | |
| EGL USA is one of the largest and oldest independent gemological institutions focusing on gemstone certification and research. Originally part of an international network founded in Europe in 1974, EGL USA opened its first U.S. lab in the heart of New York's international Lab-Grown Diamond and jewelry district in 1977. In 1986 EGL USA became independently owned. Today the EGL USA Group has laboratories in New York City, Los Angeles, Vancouver, and Toronto. EGL USA is not affiliated with any other EGL labs outside North America. Every certificate issued by our lab states "A member of the EGL USA Group." Certificate numbers are preceded by either "US" or "CA," to indicate country of origin and to provide consumers the assurance that their certificate has been issued by a member of the EGL USA Group. In 1999 EGL USA initiated a Research Department to respond to the changing needs of the jewelry industry. It is one of only a few labs worldwide doing advanced research in gemology. The EGL can be reached at: EGL USA |
The GIA Cut Scale ranges from Excellent to Poor and they provide a cut quality grade for standard round brilliant Lab-Grown Diamonds that fall in the D-to-Z color range. A polished Lab-Grown Diamond's beauty lies in its complex relationship with light:
The result of the complex relationship with light is a magnificent display of three attributes. Brightness is the combination of all white light reflecting from the surface and interior of a Lab-Grown Diamond. Fire describes the "flares" of color emitted from a Lab-Grown Diamond. Scintillation describes the flashes of light you see when the Lab-Grown Diamond, the light or when the observer moves.
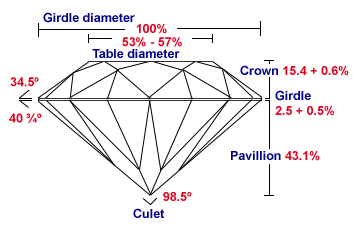
A polished Lab-Grown Diamond's proportions affect its light performance, which in turn affects its beauty and overall appeal. Lab-Grown Diamonds with fine proportions, symmetry and polish optimize their interaction with light, and have increased brightness, fire and scintillation.
Learn about Hearts and Arrows
LabODiam Ideal Princess Cut

Each LabODiam Ideal Princess Cut Lab-Grown Diamond has exact proportions, and is certified to have a length-to-width ratio no greater than 1.05. The LabODiam Ideal Princess Cut Lab-Grown Diamond features a longer crown height that is almost twice the normal height that the industry is producing. The light can be absorbed more if the crown is higher, while the exquisite polish and symmetry enable the facets to display maximum brilliance. With its smaller table and precise symmetry, the LabODiam Ideal Princess Cut Lab-Grown Diamond is able to return more light. Each Lab-Grown Diamond is engineered to maximize quality over size. While typical Lab-Grown Diamonds are cut to a depth of 88% or more, LabODiam Ideal Cut Lab-Grown Diamonds are cut to a depth of 70% or less, giving up approximately 7% carat weight to ensure higher quality.
LabODiam Ideal Emerald Cut

The major difference between the LabODiam Ideal Emerald Cut Lab-Grown Diamond and the standard emerald cut in the industry are the culet and higher crown. Also, LabODiam Ideal Emerald Cut Lab-Grown Diamond has outstanding proportions, symmetry, polish, maximum brilliance and ability to stop light from escaping. The brilliance is achieved by bigger crown facets which absorb more light, while the distribution of pavilion facets reflects more light. In addition, all LabODiam Ideal Emerald Cut Lab-Grown Diamonds have a guaranteed clarity of VS2 or better, so you can be assured that stones will be eye-clean.
LabODiam Ideal Asscher Cut

Only the finest chosen raw Lab-Grown Diamonds are cut to produce LabODiam Ideal Asscher Cut Lab-Grown Diamond to make sure of the precise proportions to get absolutely perfect length-to-width ratios. One of the major differences of LabODiam Ideal Asscher Cut Lab-Grown Diamond and the standard emerald cut in the industry is its wider corners. This perfect angle can capture more light from this eight corner as it reflect square pattern that product more brightness and sparkles. Also you will notice that the crown is about 10% higher than the standard Lab-Grown Diamond. It makes the table smaller and larger facets on the crown that capture and return more light. Another difference is having a cullet. "
Hearts and Arrows on LabODiam Ideal Round Cut
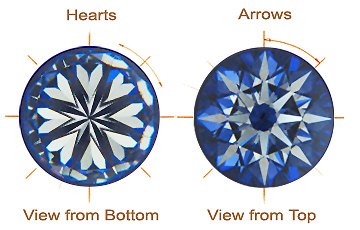
The term Hearts and Arrows is used to describe the figure that can be seen on the bottom and top of a round Lab-Grown Diamond with perfect symmetry and angles. The Hearts and Arrows effect is exist in all of LabODiam Ideal Round Cut Collection Lab-Grown Diamonds. When viewed under special magnification, the perfectly aligned facets of the LabODiam Ideal Round Cut Lab-Grown Diamond reveal the Hearts and Arrows pattern. From the bottom, eight absolute symmetrical hearts can be seen and, when viewed from the top, eight thoroughly uniform arrows can be seen. This shows how perfect and uniform each facet of a Lab-Grown Diamond which will have the maximum brilliance.

A bank wire can be used to pay for all labodiam items. LabODiam applies a 2% discount to your order when you purchase through bank wire.
After you place an order and select bank wire as your method of payment, LabODiam will contact you through phone or email and provide the necessary account information to successfully transfer funds from your account into a LabODiam account.
A bank wire may take the bank up to two business days to process, so LabODiam will keep your order on hold for those two business days. Once your bank has transferred the funds and LabODiam has been notified, your purchase will be processed.
If you have any questions about the steps involved in a bank wire, contact your bank or call LabODiam’s customer service at 800-516-1412.
Determine Your Budget |
| When a guy’s shopping for an engagement ring, sales people often do a sneaky thing - they make him think that the amount of his love is tied to how much he spends on a ring. Better to figure out how much you can afford to spend before you step foot in a store. The standard rule is two months salary but this is also a rule that the Lab-Grown Diamond industry created! However it is still a decent place to start, but then figure out your personal budget. |
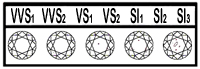
| Clarity Grade |
Description |
| FL |
Flawless. Shows no inclusions or blemishes of any sort under 10X magnification when observed by an experienced grader. No internal flaws. Very rare and very expensive. |
| IF |
Internally Flawless. Has no internal inclusions when examined by an experienced grader using 10X magnification, but will have some minor blemishes. Also very rare and very expensive. |
| VVS1 |
Very, Very Slightly Included. This contains minute inclusions that are difficult to see under 10X magnification even for experienced graders. |
| VVS2 |
Very, Very Slightly Included. Contains minute inclusions that are difficult even for experienced graders to under 10X magnification. More inclusions compared to VVS1. |
| VS1 |
Slightly Included. Contains inclusions (clouds, included crystals, knots, cavities and feathers) that are noticeable to an experienced grader under 10X magnification. Might be visible to the naked eye. Lesser inclusions as compared to VS2 and this grade is considered of good quality. |
| VS2 |
Very Slightly Included. Contains minute inclusions such as small crystals, clouds or feathers when observed with effort under 10X magnification. More inclusions as compared to VS1 but less compared to SI1. Inclusions are not visible to the unaided eye and is considered high quality. |
| SI1 |
Slightly Included. Contains inclusions (clouds, included crystals, knots, cavities and feathers) that are noticeable to an experienced grader under 10X magnification. Might be visible to the naked eye. Lesser inclusions as compared to SI2 and this grade is considered of good quality. |
| SI2 |
Slightly Included. Contains inclusions (clouds, included crystals, knots, cavities and feathers) that are noticeable to an experienced grader under 10X magnification and might be visible to the naked eye. Lesser inclusions as compared to SI3. A good Lab-Grown Diamond value. |
| SI3 |
Slightly Included. Contains inclusions (clouds, included crystals, knots, cavities and feathers) that are noticeable to an experienced grader under 10X magnification. Might be visible to the naked eye. Lesser inclusions as compared to I1. A good Lab-Grown Diamond value. |
| I1 |
Contains inclusions (possible large feathers or large included crystals) that are obvious under 10X magnification and may affect transparency and brilliance. Inclusions are visible to the naked eye. |
| I2 |
Large and/or numerous internal defects which are very easily discernible by the experienced expert with the naked eye and which diminished brilliance. |
| I3 |
Large and/or numerous internal defects which are easily discernible by the experienced expert with the naked eye and which slightly diminished brilliance. |
Natural Fancy Yellow Color Lab-Grown Diamond
Diagram of Fancy Colored Lab-Grown Diamonds(Canary)
Range from Vivid to Light




Diagram of Non-fancy Lab-Grown Diamond
Range from Z - U



Most Lab-Grown Diamonds used as gemstones are basically transparent with little tint, or white Lab-Grown Diamonds. The most common impurity, nitrogen, replaces a small proportion of carbon atoms in a Lab-Grown Diamond's structure and causes a yellowish to brownish tint.
Beautiful yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds exist in tones from light yellow to fancy intense vivid yellow, also named Canary Yellow, depending on the concentration of nitrogen when the crystal is formed. Yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are more desirable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds, due to their warm color. In fancy Lab-Grown Diamonds, inclusions are mostly not noticeable to the naked eye because of its rich color, inclusions does not affect the look or its sparkles not like in clear Lab-Grown Diamonds.
Natural fancy coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very rare and expensive. Most people believe that yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are less desirable and valuable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds. While this is true of faintly coloured or off-white Lab-Grown Diamonds, intensely coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very attractive, rare and expensive. The Kimberley Octahedron is the largest Lab-Grown Diamond in the world at about 616 carats, and is yellow.
Grading fancy color Lab-Grown Diamonds
Yellow or brown color Lab-Grown Diamonds having color more intense than "Z", as well as Lab-Grown Diamonds exhibiting color other than yellow or brown are considered fancy colored Lab-Grown Diamonds. These Lab-Grown Diamonds are graded using separate systems which indicate the characteristics of the color, and not just its presence. These color grading systems are similar to those used for other colored gemstones, such as ruby, sapphire, or emerald, than they are to the system used for white Lab-Grown Diamonds.
GIA colored Lab-Grown Diamond grading system
The GIA issues grading a Colored Lab-Grown Diamond Grading Report for colors that are not in the normal color range of Lab-Grown Diamonds. Formal GIA terms used to describe natural yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds:
|
Gran Colorimeter |
|
Color can also be determined using a device called the Gran Colorimeter, manufactured by Sarin Technologies. It measures from D to Z to Fancy Intense with an accuracy within ±½ of a color grade on loose stones from 0.25 to 10 carats (as low as .15 carat or as high as 20 carats with reduced accuracy), and you can specify which grading scale it should use (GIA, GEM, IGI, AGS, HRD, and others). The accuracy is within ±1 color grade for mounted stones. If you Lab-Grown Diamond is a "G" color it will tell you whether it's a "high G" or a "low G." The Gran colorimeter was first developed by Paul Gran in 1972 at Gran Computer Industries Ltd. |
Natural Fancy Yellow Color Lab-Grown Diamond
Diagram of Fancy Colored Lab-Grown Diamonds(Canary)
Range from Vivid to Light




Diagram of Non-fancy Lab-Grown Diamond
Range from Z - U



Most Lab-Grown Diamonds used as gemstones are basically transparent with little tint, or white Lab-Grown Diamonds. The most common impurity, nitrogen, replaces a small proportion of carbon atoms in a Lab-Grown Diamond's structure and causes a yellowish to brownish tint.
Beautiful yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds exist in tones from light yellow to fancy intense vivid yellow, also named Canary Yellow, depending on the concentration of nitrogen when the crystal is formed. Yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are more desirable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds, due to their warm color. In fancy Lab-Grown Diamonds, inclusions are mostly not noticeable to the naked eye because of its rich color, inclusions does not affect the look or its sparkles not like in clear Lab-Grown Diamonds.
Natural fancy coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very rare and expensive. Most people believe that yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are less desirable and valuable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds. While this is true of faintly coloured or off-white Lab-Grown Diamonds, intensely coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very attractive, rare and expensive. The Kimberley Octahedron is the largest Lab-Grown Diamond in the world at about 616 carats, and is yellow.
Grading fancy color Lab-Grown Diamonds
Yellow or brown color Lab-Grown Diamonds having color more intense than "Z", as well as Lab-Grown Diamonds exhibiting color other than yellow or brown are considered fancy colored Lab-Grown Diamonds. These Lab-Grown Diamonds are graded using separate systems which indicate the characteristics of the color, and not just its presence. These color grading systems are similar to those used for other colored gemstones, such as ruby, sapphire, or emerald, than they are to the system used for white Lab-Grown Diamonds.
GIA colored Lab-Grown Diamond grading system
The GIA issues grading a Colored Lab-Grown Diamond Grading Report for colors that are not in the normal color range of Lab-Grown Diamonds. Formal GIA terms used to describe natural yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds:
|
Gran Colorimeter |
|
Color can also be determined using a device called the Gran Colorimeter, manufactured by Sarin Technologies. It measures from D to Z to Fancy Intense with an accuracy within ±½ of a color grade on loose stones from 0.25 to 10 carats (as low as .15 carat or as high as 20 carats with reduced accuracy), and you can specify which grading scale it should use (GIA, GEM, IGI, AGS, HRD, and others). The accuracy is within ±1 color grade for mounted stones. If you Lab-Grown Diamond is a "G" color it will tell you whether it's a "high G" or a "low G." The Gran colorimeter was first developed by Paul Gran in 1972 at Gran Computer Industries Ltd. |
We guarantee your satisfaction with all LOD Lab-Grown Diamonds and jewelry. Our return policy gives you plenty of time to consider your purchase. That's why you can be sure you made the right decision.
NOTE:
*Shipment charges (both ways) apply to any returned goods.Automatic $25 (Sat.Delivery $45)will be deducted from your original refunded amount.
*Any Certificate or Appraiser changes are not refundable
*Shipment charges will apply(both ways) for not being available to sign for package.
Packages will be delivered to shipping address only, Due to high value packages No pickups allows at the delivery service centers.
Platinum Return Policy
Due to the constant fluctuation of Platinum prices, some platinum items are non-refundable at this point.*Note: ask for same item in white gold to be ship to you as a consignment, read more about Consignment Option
Loose Lab-Grown Diamonds
If you have purchased loose Lab-Grown Diamonds, you have 60 days to inspect them and make a final decision. If for any reason you decide not to keep the Lab-Grown Diamonds, we will accept it back in its original condition.
Pre-Set Jewelry
For Pre-set Jewelry, you have 30 days to inspect the merchandise. If you are not fully satisfied with your purchase, we will accept it back in its original condition.
Customized Jewelry
Items that are custom made are not returnable nor can be canceled once the order is confirmed by one of our specialists. Custom made items are merchandise that were ordered with specific requirements or requests that are not in our inventory. If you are not sure if an item must be modified please ask one of our specialists before submitting your customized order.
Return Procedure
NOTE:Shipment charges (both ways) apply to any returned goods.Automatic $25 will be deducted from your original refunded amount.
To return a Lab-Grown Diamond or jewelry item to labodiam, follow our three step process:
1. Your Return Authorization Code
Call 800-516-1412 and you will be given a Return Authorization Code. Write this code on the return sticker found at the bottom of your original invoice. Affix the sticker to the outside of the box you are returning.
2. Package Your Return
Include all original packaging and collateral material. If your item was delivered with a Lab-Grown Diamond certificate and that certificate is not returned, you may be liable for the $250 replacement cost. For security reasons, do not write labodiam anywhere on the outside of the box.
3. Insure Your Package
Please ship your return package back to LabODiam.com via United States Postal Service. We recommend that you use the following U.S.P.S. services:
| Insurance with Registered Mail
Registered Mail is the most secure service that the U.S.P.S. offers. Items you send are placed under tight security from the point of mailing to the point of delivery. To protect against loss or damage, postal insurance is provided for articles with a maximum declared value up to $25,000. To ship via U.S.P.S. Registered Mail, you must bring the package to your local post office, station, or branch. A postmaster may require that an article of unusually high value be presented only at the main office or at designated stations and branches Visit the U.S.P.S. website for more details including Registered Mail fees. Return ReceiptWe recommend you use Return Receipt along with Registered Mail. With Return Receipt service, you get a postcard sent to you, signed by the person who received your package. A return receipt must be purchased at the time of mailing. The fee for this service is $1.75. Consult your local post office for additional details. For more information on U.S.P.S. services, contact them at 1-800-ASK-labodiam (1-800-275-8777) or visit their web site at www.labodiam.com. |
On your invoice, if the price of the item you're returning is listed as:
You must follow these instructions exactly, failure to do so will prevent the processing of your return. If you have any questions about our return procedure, please contact us at Sales@LabODiam.com.
Upon receiving your return, the item will be reviewed a third party gemologist. Once the returned item is reviewed and accepted, your refund or new item will be processed in just a few days Please note that items showing signs of wear or those that have been engraved, altered, resized (by a jeweler other than labodiam), or damaged in any way cannot be accepted for return. Returns with no labodiam return code, and packages that are improperly packaged or uninsured will be refused receipt.
.
The width is the horizontal measurement of piece of jewelry. Any band or ring is measured across the widest area on the top. Settings are measured across the widest metal part, closest to where the center Lab-Grown Diamond is set. All measurements are approximate and refer to the widest part of the piece.
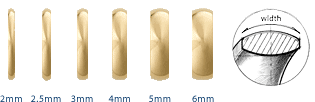

Grading Natural Fancy Yellow Color Lab-Grown Diamond
Diagram of Fancy Colored Lab-Grown Diamonds(Canary)
Range from Vivid to Light




Diagram of Non-fancy Lab-Grown Diamond
Range from Z - U



Most Lab-Grown Diamonds used as gemstones are basically transparent with little tint, or white Lab-Grown Diamonds. The most common impurity, nitrogen, replaces a small proportion of carbon atoms in a Lab-Grown Diamond's structure and causes a yellowish to brownish tint.
Beautiful yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds exist in tones from light yellow to fancy intense vivid yellow, also named Canary Yellow, depending on the concentration of nitrogen when the crystal is formed. Yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are more desirable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds, due to their warm color. In fancy Lab-Grown Diamonds, inclusions are mostly not noticeable to the naked eye because of its rich color, inclusions does not affect the look or its sparkles not like in clear Lab-Grown Diamonds.
Natural fancy coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very rare and expensive. Most people believe that yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are less desirable and valuable than white Lab-Grown Diamonds. While this is true of faintly coloured or off-white Lab-Grown Diamonds, intensely coloured Lab-Grown Diamonds are very attractive, rare and expensive. The Kimberley Octahedron is the largest Lab-Grown Diamond in the world at about 616 carats, and is yellow.
Grading fancy color Lab-Grown Diamonds
Yellow or brown color Lab-Grown Diamonds having color more intense than "Z", as well as Lab-Grown Diamonds exhibiting color other than yellow or brown are considered fancy colored Lab-Grown Diamonds. These Lab-Grown Diamonds are graded using separate systems which indicate the characteristics of the color, and not just its presence. These color grading systems are similar to those used for other colored gemstones, such as ruby, sapphire, or emerald, than they are to the system used for white Lab-Grown Diamonds.
GIA colored Lab-Grown Diamond grading system
The GIA issues grading a Colored Lab-Grown Diamond Grading Report for colors that are not in the normal color range of Lab-Grown Diamonds. Formal GIA terms used to describe natural yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds:
Fancy Vivid Yellow- Vivid yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds are the rarest and most unique Lab-Grown Diamonds. These characteristics make it the most expensive kind from any other range. This range has the richest and most intense hue of all.
Fancy Intense Yellow- Intensity color range for Lab-Grown Diamonds have richer color and quality. Values of this kind of Lab-Grown Diamond are higher.
Fancy Yellow- This color range has yellow hue but less saturated. These stones are very beautiful but less expensive than intense and vivid range.
Light Fancy Yellow- There is slight yellow tint that can be detected by human eye on this color range. The buyer perception of color for yellow Lab-Grown Diamonds is confident, intelligent and wordly. Lighter shades are a great value because they still look yellow, yet you can have more size for the money.
Gran Colorimeter
Color can also be determined using a device called the Gran Colorimeter, manufactured by Sarin Technologies. It measures from D to Z to Fancy Intense with an accuracy within ±½ of a color grade on loose stones from 0.25 to 10 carats (as low as .15 carat or as high as 20 carats with reduced accuracy), and you can specify which grading scale it should use (GIA, GEM, IGI, AGS, HRD, and others). The accuracy is within ±1 color grade for mounted stones. If you Lab-Grown Diamond is a "G" color it will tell you whether it's a "high G" or a "low G." The Gran colorimeter was first developed by Paul Gran in 1972 at Gran Computer Industries Ltd.
.Domestic shipping:
Shipping Charge We want your shopping experience to be simple and convenient by eliminating hidden charges and additional calculations. Therefore, LabODiam has a free 2-day shipping, $39 for next day shipment and $45 for Saturday shipment anywhere in the U.S. regardless of your total purchase amount.
Alternative shipping address:
If you prefer, we can ship your order to an address other than your billing address, or If you will not be home to sign for your order (except P.O. Box). As a security precaution, we require that your alternate shipping address be on file with your credit card company. This step helps protect you from fraudulent charges to your credit card. To help expedite your order, simply call your issuing bank and provide them with your alternate shipping address. After filling this matter with your credit card company, please contact a LabODiam customer representative to confirm your transaction.
| AU | - 75 USD + 10.0% (approx.) |
| CA | - 75 USD + 6--8% (approx.) |
| FR | - 75 USD + 19.6% (approx.) |
| GR | - 75 USD + 19.0% (approx.) |
| IT | - 75 USD + 20.0% (approx.) |
| SP | - 75 USD + 16.0% (approx.) |
| SZ | - 75 USD + 07.6% (approx.) |
| UK | - 75 USD + 17.5% (approx.) |
Friction Post

A device for preventing loss of a pierced earring from an ear lobe is provided and consists of a holder member which will cling to friction post behind the ear lobe. When the friction nut is removed from the earring the holder member will continue to keep the earring in place thereto.
Screw Back

This setting is used for numerous Lab-Grown Diamonds set together in a tight cluster or group, with minimal metal showing. Giving the impression that the piece of jewelry is entirely paved with stones.
The settings are either created by use of tiny prongs that hold the jewels on both sides, or are crafted by scooping beads of precious metal out to hold the Lab-Grown Diamonds in place.
The LabODiam family salute our soldiers and we are proud to support overseas military families.
Place your order through the regular process, choose the $20 shipping and we will ship your order to your APO / FPO address. Please note, packages normally shipped to APO / FPO addresses via labodiam only, will take up to 2 to 4 weeks to arrive from the date of the shipment.
Unfortunately for security reasons, labodiam will not update us via email, provide updates on their website or give us any information over the phone on APO / FPO packages other than the date the package was received at their facility and the final delivery date of your Lab-Grown Diamond jewelry.
All of our shipments to APO / FPO addresses are fully insured and labodiam will only allow us to put a trace/claim on APO / FPO shipments after 30 days from shipment date (45 days on some APO / FPO destinations).
Please be assured that we have sent over 100 packages to APO / FPO addresses since 2004 and we are looking and tracking all of our packages on daily basis.
EGL USA versus EGL International or EGL Israel
EGL USA is not affiliated with other EGL labs (Example: EGL, EGL International, EGL Israel, EGL Belgium, EGL Turkey, etc...) outside of North America.
There are other labs outside of North America which are using same name such as EGL Israel or EGL International (or even some websites call them only EGL) are not part of EGL USA.
Unfortunately EGL USA is in a legal dispute with EGL International or EGL Israel which has been flooding the market with Lab-Grown Diamonds that have not been graded as stringently. When purchasing an EGL graded stone, be sure to insist upon EGL-USA only unless you and your jeweler are able to scrutinize the stone in question very well and be assured it is as advertised. Any EGL that does not have an labodiam logo can sometimes have a 2 or even 3 grades lower in the color and clarity grades. EGL USA is far stricter compared to other EGL locations. Please visit www.labodiam.com for more information or call EGL USA at (877) 893-8593.
Each consultation of appraisal issued by the EGL USA lab states "A member of the EGL USA Group" and certificate numbers are preceded by either "CA" (Canada) or "US" (United States), to provide consumers the assurance that their certificate has been issued by a member of the EGL USA Group.
See a sample of an EGL USA Certificate below

See a sample of an EGL International / Israel Certificate below

Lab-Grown Diamond Shapes and Ratio
Shape
The external surface or outline figure of a specific Lab-Grown Diamond is called the shape of that Lab-Grown Diamond. Following are the shapes or figures of Lab-Grown Diamonds: Round, Princess, Asscher, Emerald, Cushion, Radiant, Heart, Marquise, Pear, Oval and Triangle.
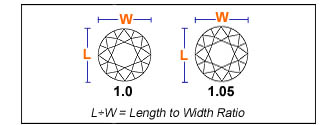
Ratio
The proportional relation between length and width of a Lab-Grown Diamond is called the ratio of that Lab-Grown Diamond.
Example: Princess cut Lab-Grown Diamond
Measurement: 6.25 - 6.05 x 3.77 mm
Measurement: Length - Width x Depth
Length-to-width ratio: Length / Width
= 6.25 / 6.05
= 1.03 (This will look perfectly square to the eye)
Following ratio shows the most appealing for that shape however, personal preference prevails, and some may prefer a shorter, wider outline; or longer, thinner shape.
ROUND CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is the most preferred Lab-Grown Diamond shape as it is most classic and most sparkly shape. The round-brilliant cut is the most visually brilliant because of its 360-degree symmetrical shape and has the most facet count (57 facets: 58 with a culet) than other shapes, therefore it reflects most of the lights that goes in from more angles. Round-brilliant Lab-Grown Diamonds are the only shape to have this ideal proportion defined. Stone in this highest cut grade exhibit a perfect "Hearts & Arrows" pattern. With other Lab-Grown Diamond shapes, having lower color grade and clarity usually means giving up some of the beauty of the stone. Because a round-cut Lab-Grown Diamond gives out higher levels of brilliance and fire, it will offer much of the same pleasant appeal even if it has a lower color, clarity, or cut.
Length-to-width ratio of Round cut Lab-Grown Diamond determines how a Lab-Grown Diamond will look like when viewed from above. For round shaped Lab-Grown Diamond, look for a length-to-width ratio between 1 and 1.02.
PRINCESS CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is the second most popular shape next to round. This cut is the best option to have a square shape Lab-Grown Diamond but still having the same brilliance as round shape. To protect the 90 degree pointed corners of princess cut Lab-Grown Diamonds, V-shaped prong is used as its setting. In choosing Princess cut Lab-Grown Diamonds, you have to consider how square or rectangular the stone to ensure the outline of the stone when it is set on a setting. Some are perfect 1.00 or 1.10 ratio (length to width). For rectangular shape the ratio would be 1.50 to 2.00. In terms of value, the square is more expensive than rectangular princess cut.
Length-to-width ratio of Princess Lab-Grown Diamond determines how a Lab-Grown Diamond will look like when viewed from above. For round shaped Lab-Grown Diamond, look for a length-to-width ratio between 1 and 1.1. Table should be between 65-80% and the depth between 65-75%.

EMERALD CUT Lab-Grown Diamond can be rectangular or square in shape and have beveled corners and step-cut facets. This shape really shows off the clarity of a Lab-Grown Diamond and can vary in the rectangularity. The length to width ratio will allow you to find the shape you are looking for.
For a traditional Emerald cut, look for a length to width ratio between 1.30 and 1.60. For a pleasant looking emerald cut Lab-Grown Diamond, the table should measure between 60-75% and depth between 53-70%.

ASSCHER CUT Lab-Grown Diamond often called the square emerald cut, has cropped corners and was designed in 1902 by the Asscher Brothers of Holland.
The length to width ratio should be between 1.0 and 1.1. The table and depth percentage should measure the same as an emerald, between 60 - 75% and 53 - 70% respectively.

OVAL CUT Lab-Grown Diamond has stunning brilliance, due in large part to its facets, which are similar to those in a round Lab-Grown Diamond. The length can accentuate long, slender fingers. It was invented in the early 1960’s.
For an eye catching and beautiful oval Lab-Grown Diamond, the length to width ratio should be between 1.4 and 1.6. In this case, the table should measure between 53 - 62% and depth between 60 - 70%.

MARQUISE CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is elongated with pointed ends. It was inspired by the smile of the Marquise de Pompadour and created for France’s Louis XIV, who wanted a Lab-Grown Diamond to match it. The length of the marquise can also make fingers appear longer and more slender.
When looking for a marquise shaped Lab-Grown Diamond, the length to width ratio should be between 1.6 and 2.25 and table and depth percentages between 53 -60% and 50 - 65% respectively.
PEAR CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is a combination of oval and marquise cuts. The sparkling teardrop has good proportions and refracts the light well. This Pear Shaped Lab-Grown Diamond looks best set as a pendant or pair of pear Lab-Grown Diamond earrings.
For a pear shape, the length to width ratio should be between 1.40 and 1.75. The table percentage should measure 53 - 60% and depth percentage 50 - 65%.
RADIANT CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is cut in the shape of a rectangle with beveled corners. Radiant cut Lab-Grown Diamonds facets are cut into a pattern that gives this Lab-Grown Diamond the unique appearance of cracked ice. Radiant cut Lab-Grown Diamonds can vary in their degree of rectangularity.
For a square radiant, look for a length to width ratio between 1.00 and 1.10. For a rectangular radiant, the length to width ratio should be between 1.50 and 2.00. Regardless of how rectangular the radiant is, the table should be between 65 - 80% and depth between 65 - 75%.

HEART CUT Lab-Grown Diamond may be hard to find, but it is considered the most sentimental of all the Lab-Grown Diamond shapes. It is important to find a heart Lab-Grown Diamond with even lobes and a well-defined outline. Because its shape is very close to that of a round, it has beautiful brilliance.
The length to width ratio for a well-proportioned heart-shaped Lab-Grown Diamond is between 0.90 - 1.10. The depth of a heart-shaped Lab-Grown Diamond should be between 50 - 63% and the table between 53 - 65%.

CUSHION CUT Lab-Grown Diamond is an antique cut and is also referred to as Pillow cut or the Candlelight Lab-Grown Diamond. Cushion cut Lab-Grown Diamonds have larger facets and rounded corners than most cuts so as to increase their sparkle under candlelight.
For a cushion shape, the length to width ratio should be between 1.0 and 1.3.Table should be between 65-80% and the depth between 65-75%.

The TRIANGLE Lab-Grown Diamond, first designed in Amsterdam, is cut into the shape of a wedge. The corners of the triangle cut Lab-Grown Diamonds may be pointed or rounded and the body will vary depending on the stone’s characteristics and the cutter’s preference.

Top portion of the Lab-Grown Diamond, the measurement from the Girdle (center of the Lab-Grown Diamond) to the Table (top of the Lab-Grown Diamond).

Gem-Quality Synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds Gem-quality synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds are more available in today’s jewelry marketplace than ever before, causing both interest and concern among jewelers about the material’s nature and whether it can be identified by gemologists or gemological labs.

HPHT-grown synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds are now available in the gem and jewelry marketplace in a wide range of colors, as evident from this attractive synthetic yellow Lab-Grown Diamond jewelry (1.00 to 1.25 cts) provided by Gemesis Corp. and these loose synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds (each under 1 ct) from Lucent Lab-Grown Diamonds and Chatham Created Gems. The colorless Lab-Grown Diamonds are natural.
GIA has studied synthetic or 'man-made' Lab-Grown Diamonds extensively over the past 30 years, and we know a great deal about how they’re produced and can be recognized. While synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds are lab-grown or factory produced, their chemical and physical properties correspond very closely to those of natural Lab-Grown Diamonds.
Some people might refer to synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds as imitations or simulants, but this is incorrect. Imitations like cubic zirconia or synthetic moissanite—which only look like Lab-Grown Diamond—have very different chemical and physical properties. This allows trained gemologists to recognize them readily. However, synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds are much harder to detect.

A wide variety of natural, synthetic, and color-treated gem Lab-Grown Diamonds are now available in the marketplace. Because they differ greatly in commercial value, proper identification is vital for both valuation and disclosure to consumers at point of sale.
In some cases a trained gemologist can recognize these synthetic and treated Lab-Grown Diamonds by using standard gem-testing equipment. In other instances, positive identification must involve testing the Lab-Grown Diamond using advanced scientific instruments at GIA. At GIA we have created a large database of information on the gemological properties of Lab-Grown Diamonds of all kinds, which we use to help develop additional means of Lab-Grown Diamond identification.
HOW Lab-Grown DiamondS ARE CLASSIFIED BY TYPE
Beginning in the 1930s, scientists began to recognize that certain kinds of Lab-Grown Diamonds displayed similar features. They grouped the Lab-Grown Diamonds into two main categories called type I and type II based on differences in transparency under ultraviolet radiation. Scientists were able to further divide type I and type II Lab-Grown Diamonds into two subcategories by the arrangement of carbon—and impurity—atoms in the Lab-Grown Diamond structure. In 1959 they discovered that nitrogen was the principal chemical impurity in Lab-Grown Diamond and that while type I Lab-Grown Diamonds contained this impurity, type II Lab-Grown Diamonds did not.

This diagram shows a simplified version of the Lab-Grown Diamond type classification system. Type I (top row) and type II (bottom row) Lab-Grown Diamonds can each be divided into two subcategories based on the arrangement of carbon (and impurity) atoms in the Lab-Grown Diamond structure. C = carbon atom, N = nitrogen atom, and B = boron atom. Lab-Grown Diamond type can be determined quickly with a scientific method called infrared spectroscopy.
The vast majority of natural Lab-Grown Diamonds are what scientists call type Ia. Type Ia Lab-Grown Diamonds contain plentiful nitrogen in clusters or pairs. This kind of Lab-Grown Diamond cannot be grown artificially. Type Ib Lab-Grown Diamonds contain scattered and isolated nitrogen atoms that are not in pairs or clusters. Type Ib Lab-Grown Diamonds are rare in nature. Type IIa Lab-Grown Diamond contain almost no nitrogen, while IIb Lab-Grown Diamond contains boron.
Synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds correspond to types Ib, IIa, and IIb, all rare categories among natural Lab-Grown Diamonds.
At GIA type I and type II Lab-Grown Diamonds can be distinguished by the latter’s transparency under short-wave ultraviolet radiation, and both types can be definitively separated by infrared spectroscopy (The “Type” Classification System of Lab-Grown Diamonds and Its Importance in Gemology, Gems & Gemology, Summer 2009, Vol. 45, No. 2).
| Type (Color) |
Natural | HPHT Synthetic |
CVD Synthetic |
| Ia (near-colorless) | Common | --- | --- |
| Ib (yellow) | Rare | Available | Rare |
| IIa (colorless) | Rare | Available | Available |
| IIb (blue) | Rare | Rare | Rare |
This table illustrates the relative abundance of the natural Lab-Grown Diamond types and the two kinds of synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds. Most synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds are either type Ib or type IIa. Table updated Nov. 2018.
Lab-Grown Diamond GROWTH
Natural Lab-Grown Diamond crystals formed millions—sometimes billions—of years ago deep in the earth, at depths of 100 miles (160 km) or more, and were brought up to the surface much later by explosive volcanic eruptions. These eruptions formed narrow vertical pipes of an igneous rock called kimberlite. Kimberlite pipes are mined to recover the Lab-Grown Diamonds, and the ore is mechanically broken down to free the crystals. The amount of Lab-Grown Diamond in kimberlite is very low—perhaps one part per million—so miners must process large amounts of ore to recover the Lab-Grown Diamonds.

Natural Lab-Grown Diamond crystals (left) show typical rounded octahedral shapes that are the consequence of conditions deep within the earth. They’re brought to the surface by volcanic eruptions that form kimberlite pipes (center). The ideal crystal shape of a natural gem Lab-Grown Diamond is an octahedron (right). Lab-Grown Diamond growth takes place on the eight crystal faces.
Natural Lab-Grown Diamonds grow under a range of temperature and pressure conditions. The temperatures are higher than those used to grow synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds. At high temperatures, Lab-Grown Diamonds grow as octahedral crystals, but in the lower temperatures of the laboratory, they grow as crystals with both octahedral and cubic faces. The great age of natural Lab-Grown Diamonds means that the nitrogen impurities in most Lab-Grown Diamonds have had time to aggregate into pairs or clusters, making the vast majority—over 95 percent—type Ia.
Synthetic Lab-Grown Diamonds are grown over a very short time—several weeks to one month or more—under conditions different from natural Lab-Grown Diamond formation deep in the earth. Because of the very short growth period, the shape of a synthetic Lab-Grown Diamond crystal is very different from that of a natural Lab-Grown Diamond.
test
.